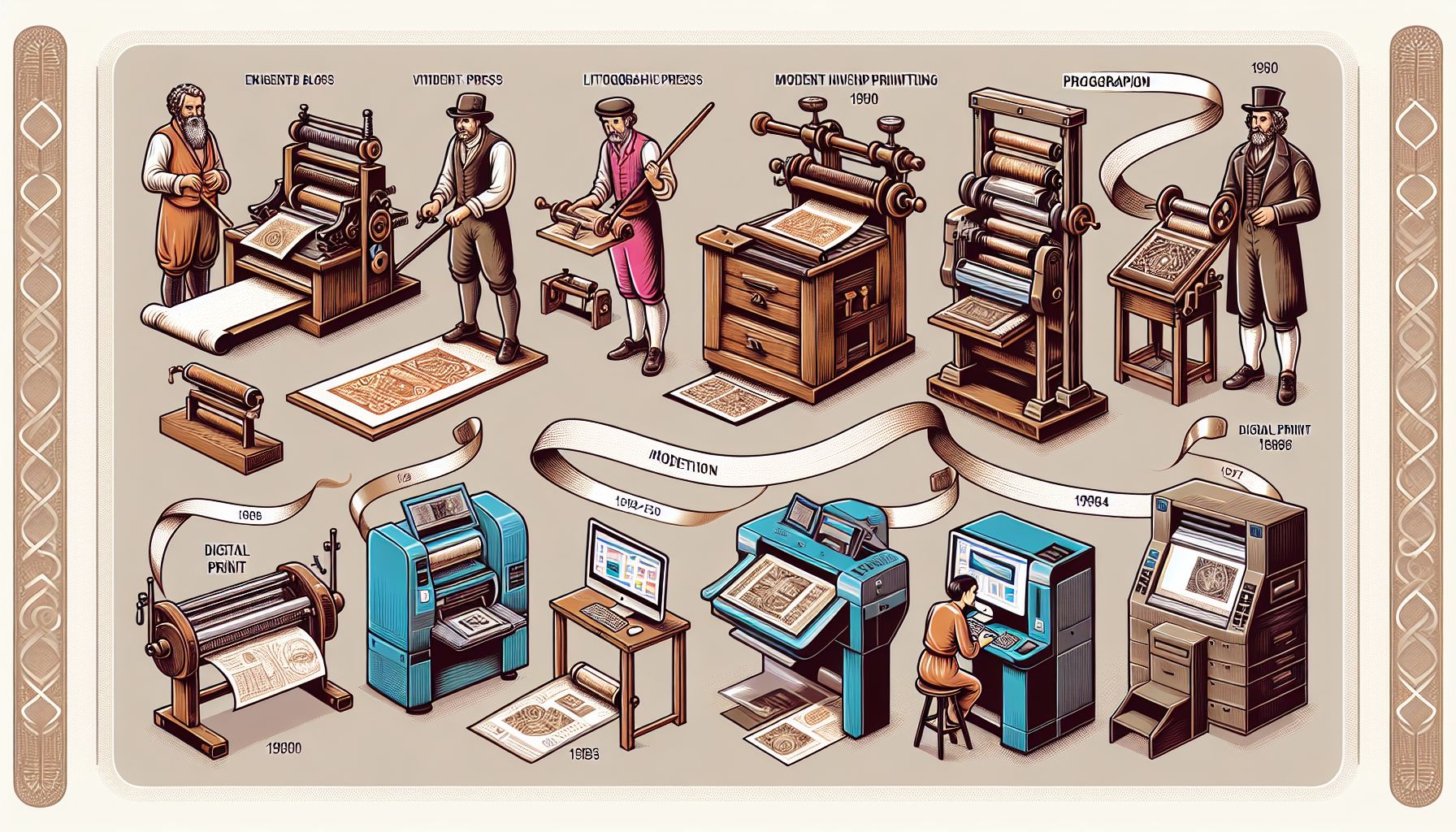
Printing techniques have come a long way since the inception of the ancient woodblock printing method in China during the Tang Dynasty. From Gutenberg’s revolutionary movable type printing press to the modern digital printers we use today, printing techniques have constantly evolved to meet the growing demands of businesses and individuals alike. Whether you are printing business cards, posters, or books, understanding the different printing techniques available can help you make informed decisions and achieve the desired outcome. In this article, we will explore some of the most common printing techniques used today, from traditional offset printing to the more recent digital printing methods.
The Evolution of Printing Techniques
Before diving into the different printing techniques available, let’s take a moment to appreciate the groundbreaking innovations that have shaped the history of printing. Johannes Gutenberg’s invention of the movable type printing press in the 15th century paved the way for mass production of printed materials, revolutionizing the spread of knowledge and cultural exchange. This technique involved arranging individual metal or wooden letters, numbers, and symbols in a composing stick to create a locked printable form. Ink was then applied to the form before pressing it onto paper.
Since Gutenberg’s innovation, various printing techniques have emerged, each with its unique process, advantages, and limitations. These techniques are primarily categorized into two broad categories: traditional printing methods and digital printing methods.
Traditional Printing Techniques
1. Offset Printing
Offset printing, also known as lithography, is one of the most widely used traditional printing techniques. It involves transferring images or text from a metal plate to a rubber blanket, then onto the printing surface. Offset printing offers excellent image quality and is ideal for high-volume printing projects, such as magazines, newspapers, and brochures. The process begins with creating printing plates by exposing photosensitive materials to film or digitally generated images. The plates are then mounted on rotating cylinders in the printing press, and the inked image is transferred onto the paper through a series of rollers.
2. Letterpress Printing
Letterpress printing, once the primary printing method, is now mainly used for specialty projects due to its labor-intensive nature. This technique involves applying ink to a raised surface, often using movable type or custom-engraved plates. The inked surface is then pressed onto paper, creating a debossed effect. Letterpress printing is known for its distinctive, tactile quality and is often favored for elegant wedding invitations, business cards, and limited-edition art prints.
3. Flexography
Flexography, also known as flexo printing, is a versatile technique commonly used for packaging materials, labels, and newspapers. It utilizes flexible relief plates made of rubber or photopolymer materials. The inked plates are mounted on rotating cylinders, and the printing surface is pressed against them using an anilox roller, which transfers a controlled amount of ink. Flexography offers fast printing speeds and is ideal for large-scale production due to its ability to print on various substrates.
4. Gravure Printing
Gravure printing, often referred to as intaglio printing, is commonly used for producing high-quality prints in magazines, catalogs, and packaging. It involves engraving or etching an image onto a cylindrical plate, with each cell representing a specific color or shade. The plate is then inked, and the excess ink is wiped away, leaving ink only in the engraved cells. The paper is pressed against the plate, and the ink transfers through the action of pressure.
Digital Printing Techniques
With the advancement of digital technology, new printing techniques have emerged, offering greater flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and customization options.
1. Inkjet Printing
Inkjet printing is perhaps the most commonly used digital printing technique. It involves propelling tiny droplets of ink onto the printing surface to create an image. Inkjet printers are highly versatile, capable of producing high-resolution prints with vibrant colors, making them suitable for various applications, from home and office use to professional photography prints. Inkjet printing also allows for cost-effective short-run printing, as there is no need for extensive setup and plate-making.
2. Laser Printing
Laser printing, widely used in offices and print shops, relies on electrostatic charges to transfer toner onto the printing surface. Laser printers use a laser beam to create a static charge pattern on a drum, attracting toner particles and transferring them onto the paper. This method offers high printing speeds and is particularly efficient for text-heavy documents. However, laser printing typically produces a glossy finish and may not be suitable for certain types of artwork or photography.
3. Digital Offset Printing
Combining the best of both traditional and digital printing, digital offset printing offers the high image quality of offset printing with the advantages of digital technology. This technique involves transferring an image from a computer directly to the printing plate, skipping the need for films or other physical intermediaries. Digital offset printing is ideal for short to medium print runs and provides accurate color reproduction and fine details.
Choosing the Right Printing Technique
Selecting the most suitable printing technique depends on various factors, such as the intended use, budget, turnaround time, and desired quality. For large-scale projects requiring high-volume output, offset or flexography printing might be the optimal choice. Letterpress and gravure printing are ideal for projects that demand superior quality and tactile appeal. On the other hand, digital printing techniques like inkjet and laser printing offer flexibility for short runs and customization.
In conclusion, with a plethora of printing techniques available today, understanding their strengths and limitations can empower you to make informed decisions. Whether you are a business owner in need of marketing materials or an individual pursuing a creative project, choosing the right printing technique can elevate the quality, impact, and success of your endeavor. Consider the factors mentioned and explore various printing options to find the perfect fit for your specific needs. Embrace the evolution of printing techniques and embark on a journey of endless possibilities.